Lighting Control Methods
Analogue control
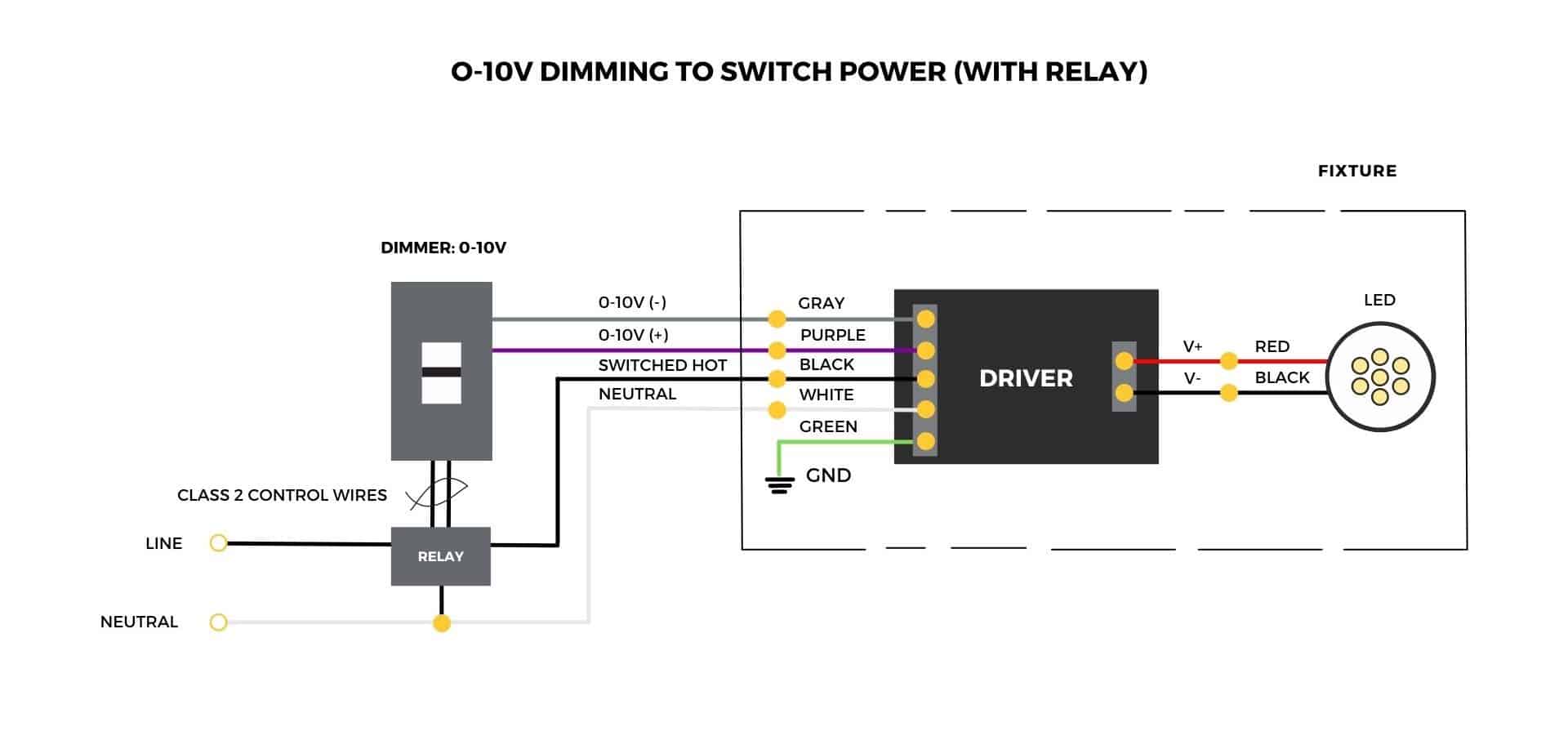
0-10 V
0-10 V dimming controls the lighting intensity by adjusting DC voltage that provided for lighting fixtures ranging from 0 V to 10 V.
Advantages
- The simplicity of the lighting system is easy to understand.
- Suitable to control LED.
Note:
- The control signal is a DC voltage that varies between 0 and 10 volts.
- Light output 100% at 10 V and 0% at 0 V.

1–10 V
1-10 V dimming controls the lighting intensity by adjusting DC voltage that provided for lighting fixtures ranging from 1 V to 10 V.
Advantages
- The simplicity of the lighting system is easy to understand.
- Suitable to control LED.
Note:
- The control signal is a DC voltage that varies between 1 and 10 volts.
- Light output 100% at 10 V and 10% at 1 V.
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
PWM is used to control the output voltage of the converter by modulating the width of the pulse of the output waveform.
Advantages
- Low power consumption.
- Efficiency up to 90%.
- Easy to separate a signal.
- Little heat whilst working.
- Noise interference is less.
- High-power handling capacity.
- The requirement for a viable filter is less.
- Significant reduction in total harmonic distortion of load current.
- Amplitude and frequency can be controlled fairly independently.
- Synchronization between the transmitter and the receiver is not required.
Note:
- PWM speed is 50-90 Hz (50 f/s).
- You can see a flicker when recording video.

TRIAC (Triode AC Switch)
TRIAC is the most commonly used semiconductor device for switching and power control of AC systems as the Triac can be switched “ON”
by either a positive or negative Gate pulse, regardless of the polarity of the AC supply at that time.
Advantages
- Ability to use with 230 V.
- Switching and power control of AC systems.
- It can be triggered with the positive or negative polarity of gate pulses.
- It requires only a single heat sink of a slightly larger size, whereas, for SCR (silicon controlled rectifier), two heat sinks should be required
of a smaller size. - It requires a single fuse for protection.
- A safe breakdown in either direction is possible but SCR (silicon controlled rectifier) protection should be given with a parallel diode.
Note:
- Low efficiency and may flicker if turned on together with other electronic devices.

Digital control
DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface)
The Digital Addressable Lighting Interface (DALI) is a digital serial control protocol for architectural lighting. DALI standard: IEC 60929.
It operates using a 2-wire bus for communication. (Command/Data) as well as supplying power to DALI devices, which is can vary though is typically about
16 V when there is no communication. The DALI bus command provides facility to control, configure, and query the product.
Advantages
- Increased energy savings.
- Control of individual lights and dynamic creation of groups (circuits).
- Ability to configure & reconfiguration for changing scenarios.
- Simple interface with control and building management systems.
- Each unit in the system is addressable.
- Easy to modify and expand.
- Only one pair of control conductors even in multi-channel systems give lower installation costs.
- Polarity-free control conductor reduces the risk of wrong connections.
- Can be controlled via an interface by a computer.
- Can be connected to a BMS system (LonWorks, EIB) via a gateway.
Note:
- Only 64 ballasts per DALI bus (interface).
- Only 16 groups per interface.
- Only 16 scenes per interface.
- Ballast configuration (including address), groups and scenes is uploaded to and stored in the ballasts themselves.
- Topology-free DALI bus operates at very low data rates.
- Command-based protocol, ballasts perform fades and maintain levels.
- Only certain discrete fade values are permitted.
- As a result, the DALI protocol is not suitable for rendering effects and media, programming is restricted purely to recalling lighting levels via
the Set Level and DALI Scene presets. - The system must be programmed before commissioning.
- Programming is performed in different ways for products from different manufacturers.
- Max 64 addresses/system (Note that the interface for programming via a computer requires an address).
- Large systems can be built up via software/servers/gateways. This type of system usually utilises existing data networks (TCP/IP).
An example of this type of system is winDIM@net from Tridonic.

DMX 512 (Digital Multiplex)
DMX is an internationally recognised protocol used to control lighting. In accordance with ANSI and maintained by ESTA.
Advantages
- Easy to use protocol.
- Suitable to use for large installations and lighting setups.
- Known systems with many control options, lightbox, software, etc.
- It has more channels than analog and can be used for any console.
- No ability to set address or multiple values of driver/controller.
- Each luminaire must be physically accessible for setting up, for example by operating a dip switch or other interface, which can be difficult
if the luminaires have already been installed. - No possibility of receiving operational or fault states back at the console.
Note:
- Special requirements for control cable and installation.
- A terminator is a stand-alone male connector with an integral 120 Ω resistor connected across the primary data signal pair.

RDM (Remote Device Management)
RDM is ANSI E1.20 Remote Device Management offers an improvement to the DMX protocol by adding bidirectional communication between lighting controllers (or systems) and connected RDM compatible devices.
Advantages
- Access to driver/controller address settings via 3 core data cables.
- The console can search the DMX Universe for all connected devices and then automatically patch address them.
- RDM devices can be firmware upgraded via the DMX512 signal.
- RDM devices can send status and fault information back to the console.
- Bidirectional communication enables easier integration of DMX installations with sophisticated ethernet protocols such as Art-Net or sACN
Note:
- This can be achieved using standard DMX512 cables, providing that all three cables are connected at the end.
- DMX512 typically only sends commands from the controller to the source, RDM facilitates bidirectional communication which provides many advantages and is especially useful for addressing settings and other functions.
Zigbee
Advantages
- Zigbee has a flexible network structure.
- It has very long battery life.
- Zigbee has a mesh network topology with low cost, multi hop data transmission and is power effective.
- It is less complex than Bluetooth.
- Easy to install.
- Zigbee supports a large number of nodes.
- It is a short working period results in power saving and power consumption of communication.
Note:
- 2.4 GHz
- 915 GHz
- 868 MHz
Bluetooth/Wifi
Advantages
- No wires are required.
- Thousands of nodes per network.
- Use of standard smartphone.
- No single point of failure.
Note:
- 2.4 GHz


